Smart Ways to Find the Horizontal Asymptote in 2025: A Practical Guide to Modern Methods
Smart Ways to Find the Horizontal Asymptote in 2025
Understanding the horizontal asymptote is crucial for grasping the behavior of rational functions as they approach infinity. This practical guide discusses modern methods for accurately determining horizontal asymptotes, emphasizing rules, calculations, and behavior analysis. With many real-world applications and teaching contexts covered, by the end of this article, you’ll be well-equipped to identify and utilize horizontal asymptotes in various mathematical situations.
Understanding Horizontal Asymptotes
The horizontal asymptote definition refers to a horizontal line that the graph of a function approaches as the input values approach infinity or negative infinity. By identifying the asymptotic behavior of a function, we can predict its trends without graphing the entire function. It’s vital in the analysis of rational functions, which take the form of the ratio of two polynomials. The important aspect to remember when finding a horizontal asymptote is to analyze the degrees of the polynomials involved.
Horizontal Asymptote Rules
To effectively determine a horizontal asymptote, apply the horizontal asymptote rules. Here’s a quick breakdown based on the degrees of the polynomial in the numerator (top) and the denominator (bottom):
- If the degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote is at y = 0.
- If the degree of the numerator equals the degree of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote can be found by taking the ratio of the leading coefficients.
- If the degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator, then there is no horizontal asymptote. Instead, there may be an oblique asymptote.
Understanding these rules is a strong first step in calculating horizontal asymptote values accurately.
Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes
The calculations for horizontal asymptotes often invoke limits and horizontal asymptotes. When the function approaches infinity, we can express this using limit notation. For example, in determining the horizontal asymptote of the function f(x) = (3x^2 + 2)/(5x^2 + 1), we can establish:
lim(x→∞) f(x) = lim (3/5) = 3/5. This indicates a horizontal asymptote at y = 3/5. Evaluating limits is a foundational step in understanding the end behavior of functions.
Finding Horizontal Asymptotes in Rational Functions
Rational functions are particularly important when discussing horizontal asymptote calculation. These functions show distinct end behaviors that can reveal key characteristics. Setting up rational expressions allows you to analyze the growth rates for large absolute values of input.
Rational Expressions and Their Behaviors
When working with rational expressions, identifying horizontal asymptotes helps in understanding their respective behavior at infinity. For instance, in the rational function example above, when considering limits of large values, the lesser terms vanish, revealing the gradual approach to the horizontal asymptote.
In real-world paradigms, the evaluation of such behaviors aids in predicting outcomes or trends, such as population growth modeling, wherein resources become limited.
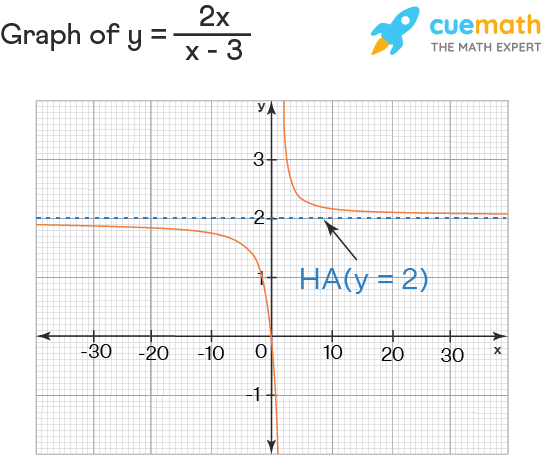
Graphical Representation of the Horizontal Asymptote
A horizontal asymptote graph, a critical asset in calculus, visually portrays how a function behaves as it approaches positive or negative infinity. When graphing function trends, the horizontal asymptote typically crosses at y = value if limits approach this constant. The graph provides insights into where functions stabilize at large inputs, providing a clear visual marker and confidence in initial assessments.
Applications of Horizontal Asymptotes
The horizontal asymptote application transcends classroom learning, finding relevance in various fields such as economics and physics. Understanding the limiting behaviors defined by asymptotes allows the comprehension of systems under various conditions and can lead to influential practical applications.
Practical Examples of Horizontal Asymptotes
Let’s explore an example relevant in business models:
– **Example Function:** The profit function is modeled as P(x) = (100x)/(x^2 + 10).
To determine its horizontal asymptote, find lim(x→∞) P(x). As x approaches infinity, we capture coefficients 100 and 1, resulting in P(x) approaching 0. The horizontal asymptote is thus y = 0. This example emphasizes that profitability battles limitations significantly influenced by operational bottlenecks.
Behavior Analysis in Problem Solving
Lastly, honing your skills in analyzing rational functions through a behavioral lens will enhance problem-solving abilities. Identifying horizontal asymptotes can clarify won ambiguities during curve sketching or when using graphing rational functions.
By understanding how functions approach a trend—or fail to attain a limit—you can make educated decisions regarding function limits when modeling business or scientific applications.
Key Takeaways
- The rules for determining horizontal asymptotes based on polynomial degrees revolve around zero, leading coefficient ratios, and behavior of growth.
- Understanding limits is invaluable for calculating horizontal asymptotes and grasping function trends.
- The ability to graph and interpret horizontal asymptotes underlines significant real-world scenarios, allowing for prediction and trend analysis.
- Studying both rational and polynomial function behaviors plays a pivotal role in algebraic expressions and calculus applications.
FAQ
1. What is the definition of limits in the context of horizontal asymptotes?
The definition of limits relates to the value that a function approaches as the input gets arbitrarily large or small. For horizontal asymptotes, we use limits by examining functions as x approaches ±∞ to determine if they stabilize at a specific y-value.
2. How do horizontal and vertical asymptotes differ?
Vertical and horizontal asymptotes serve different purposes. Vertical asymptotes indicate points where a function goes to infinity, while horizontal asymptotes describe stable values as input grows large. Knowing both aids in comprehensive graph analysis.
3. Can all functions have horizontal asymptotes?
No, not all functions have horizontal asymptotes. Only certain types of functions, particularly rational functions, exhibit horizontal asymptotic behavior based on the polynomial’s degree. Functions can also present slant or no asymptotes if they grow unbounded.
4. What is an improper fraction’s horizontal asymptote?
Improper fractions horizontal asymptote follows the same logic as events defined by rational functions. If the degree of the numerator exceeds that of the denominator (and of equal degrees), then identify the horizontal asymptote through the ratio of coefficients from the highest power term.
5. How to utilize the horizontal line test in function analysis?
The horizontal line test helps determine if a function has an inverse. If any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once, the function fails this test. Hence relating to horizontal asymptotes, a single y-value here reflects unique behavior through rational functions.
6. What role do horizontal asymptotes play in polynomial functions?
In assessing polynomial functions, horizontal asymptotes analyze long-term behavior as the inputs grow large, providing insights into whether the function has a limiting value as it approaches ±∞. This insight is crucial for function analysis during evaluations in modern calculus.
—
For more resources on the topic, you can check out the following links:
1. [Link to More Information on Finding Horizontal Asymptotes](https://fixace.info/?p=1124)
2. [Link to In-Depth Explorations of Functions](https://fixace.info/?p=1129)