How to Efficiently Calculate the Volume of a Rectangular Prism in 2025
“`html
How to Efficiently Calculate the Volume of a Rectangular Prism
Understanding the Formula for Rectangular Prism Volume
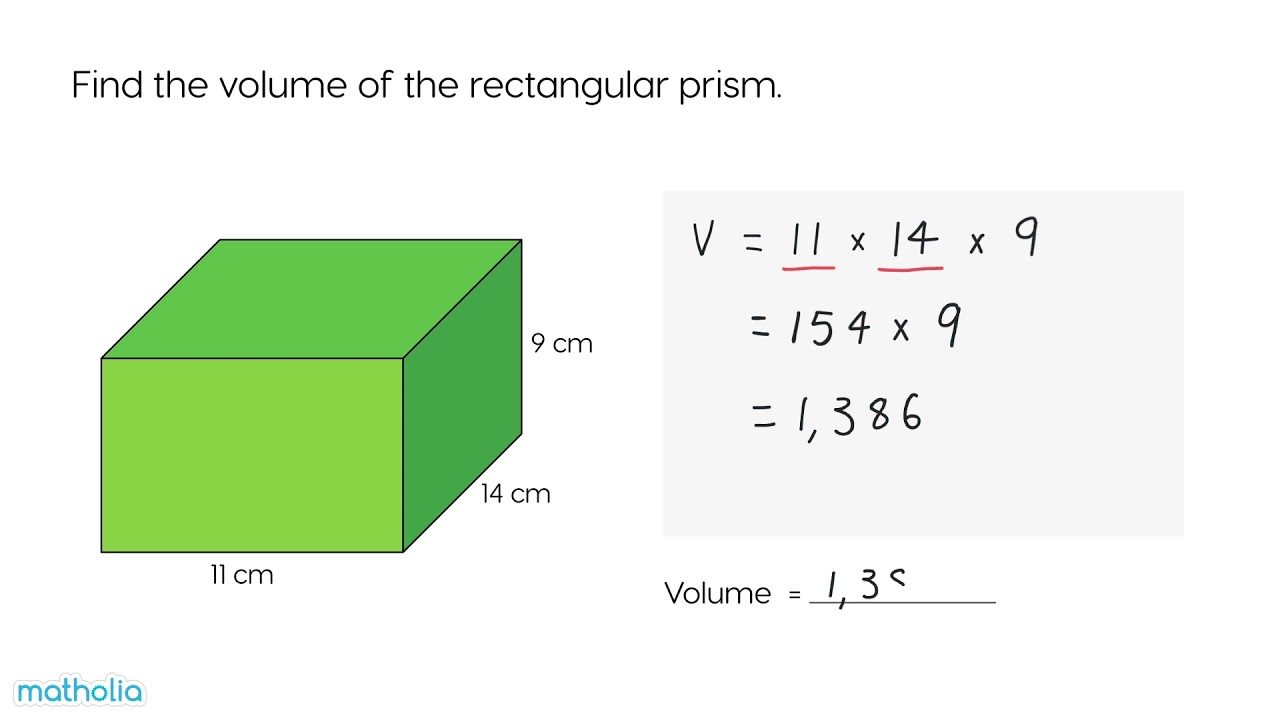
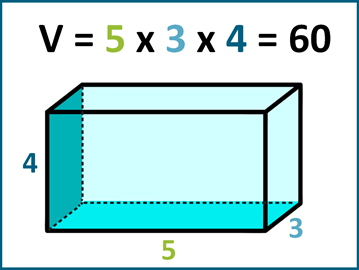
The **volume of a rectangular prism** can be calculated using a simple formula: Volume = Length × Width × Height. This formula derives from the basic principles of geometry, where the rectangular prism is defined by its three dimensions: length, width, and height, often referred to as the **physical dimensions of a prism**. It’s crucial to ensure all measurements are in the same unit before performing any calculations, as mixing units can lead to inaccurate results. Understanding how these dimensions interact is fundamental in **finding volume of prism** and applying volume concepts in various practical scenarios.
Application of the Volume Formula
To apply the formula in a real-world situation, consider a rectangular box with a length of 10 cm, a width of 5 cm, and a height of 2 cm. Plugging these values into our formula gives us: Volume = 10 cm × 5 cm × 2 cm = 100 cm³. Furthermore, manipulating this formula for diverse shapes can aid students in grasping **understanding volume in geometry**. Classroom activities that involve packaging objects, such as gifts or ingredients for baking, can effectively demonstrate how to calculate the volume of rectangular solids and create a tangible learning experience.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Volume
While calculating the **volume of 3D objects**, many students mistakenly change the units or fail to physicalize measurements accurately. When working with real-world applications of volume, it’s essential to emphasize the importance of precision and consistency in measurements. Before performing a calculation, ensuring that each dimension adheres strictly to a uniform unit of measurement can mitigate errors—a critical aspect in educational resources dedicated to teaching volume calculations.
Interactive Volume Lessons
To reinforce learning, teachers can turn the calculation of volume into a fun, engaging activity. For instance, utilizing visual aids for volume, such as 3D models or digital simulations, can significantly enhance students’ understanding. This approach not only makes the learning more interactive but also puts emphasis on **dimensional analysis for volume**. By incorporating educational technology into lessons, students can visualize volume changes and grasp how dimensions interact within calculations.
Practical Applications of Volume Calculation Techniques
The concept of calculating the volume has versatile applications that span across various fields, including architecture, engineering, and environmental science. Understanding the dimensions of a rectangular prism and successfully executing the formula often exemplifies foundational geometry skills essential for more complex topics in mathematics. By exploring these practical applications of volume calculation, students get a taste of how volume concepts relate to real-world challenges and design projects.
Using Volume in Architecture
In architecture, calculating the volume of rectangular shapes can inform the design and planning of spaces. For example, when designing a room, knowing the volume aids in determining how much air circulation is needed or how many materials are necessary for construction. A well-architectured space ensures not just aesthetic appeal but also functionality by incorporating **volume vs. surface area in prisms** principles into construction planning.
Volume in Environmental Science
In environmental science, understanding volume is crucial for determining capacities related to natural bodies, like water reservoirs or soil saturation levels. Accurate **volume calculation** techniques enable researchers to estimate quantities essential for ecological studies, ensuring higher efficiency when planning conservation or restoration projects. This emphasizes the relevance of **volumetric analysis in science** and enhances the spatial awareness necessary for tackling ecological challenges.
Hands-on Volume Exploration Activities
Engaging students in hands-on activities such as measuring water in containers of various shapes can foster better understanding. By employing **volume calculation examples** using familiar objects, educators can illustrate the process of **calculating prism volume** practically. These activities promote interest and curiosity about how volume relates to **everyday life** while reinforcing academic knowledge through tactile learning.
Dimensional Analysis for Volume Understanding in Geometry
Dimensional analysis is a powerful tool in geometry that promotes understanding the relationship between volume and physical dimensions such as width, height, and length. This analytical approach not only deepens comprehension for students but also serves practical purposes in career fields requiring volumetric calculations. Understanding how to scale shapes proportionately while preserving volume can transfer directly to disciplines such as architecture and fluid dynamics.
Understanding Volume Measurement Standards
Volume measurement varies widely in application and context. Familiarizing students with **units of volume measurement**, such as liters and cubic centimeters, enables them to make better calculations based on context. For tasks involving volume conversion, keeping reference charts handy aids learners in making necessary adjustments quickly. Reinforcing this through practice ensures students regard volumetric methods as adaptable and transferable skills.
Comparing Volumes of Different Shapes
Another practical approach to understanding volume is comparing that of different shapes. For instance, engaging students in projects where they calculate and compare **rectangular prism volume vs. other 3D shapes** like spheres or cylinders can highlight the distinctions and applications of each. This also introduces students to essential concepts like **volume and capacity in geometry**, fostering critical thinking and comprehension skills around volume across mediums.
Common Volume Miscalculations
As students learn to calculate the volume of a rectangular prism, it’s important to address common **volume calculation mistakes**. These often stem from incorrect unit usage or misunderstanding the formula. Encouraging errors as learning opportunities provides students with insights into practicing their calculations and retaining their learning. Assessing homework or projects focusing on practical scenarios assists students in recognizing these pitfalls while applying corrections confidently alongside their peers.
Key Takeaways
- The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is Volume = Length × Width × Height.
- Practical applications of volume span across fields such as architecture and environmental science.
- Hands-on activities enhance learning by allowing students to practice and visualize volume.
- Understanding and using consistent volume measurement units is crucial for accuracy.
- Common miscalculations can be mitigated through educational strategies that promote an engaging atmosphere.
FAQ
1. What are the key dimensions needed to find the volume of a rectangular prism?
The key dimensions for calculating the **volume of a rectangular prism** are its length, width, and height. These three measurements must be consistent units to arrive at accurate volume calculations.
2. Can the volume formula for a rectangular prism be applied to irregular shapes?
While the standard **volume formula** applies to rectangular prisms, irregular shapes can often be decomposed into regular shapes to calculate their volume. This method demonstrates **geometric prism properties** in practice.
3. How do volume calculations differ from surface area calculations?
Volume calculations focus on the amount of three-dimensional space a shape occupies, while surface area measures the total area covering the object’s surface. This highlights the concept of **volume vs. surface area in prisms** within geometry.
4. What units are commonly used for measuring volume?
Common units of volume include cubic centimeters (cm³), liters, and gallons. Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for accurate **units of measurement in volume** calculations.
5. Why is it important to visualize volume in geometry?
Visualizing volume in geometry helps in comprehensively understanding the implications of volumetric measurements in real-life contexts. Visualization aids in grasping complex concepts like **how to calculate volume of rectangular prism** efficiently and creatively.
6. What are some effective teaching strategies for volume calculations?
Effective strategies involve hands-on learning, using visual aids, incorporating technology, and providing real-world examples where volume calculations are applicable. Encouraging interactive lessons engages students more deeply in **educational resources for volume**.
7. How can students avoid common mistakes in volume measurements?
Students can avoid common mistakes by consistently checking unit measurements and ensuring all calculations are performed using the same systems. It’s also beneficial to practice with various real-life scenarios to reinforce **calculating prism volume** accuracy.
“`