How to Properly Calculate Percent Yield for Effective Results in 2025
How to Properly Calculate Percent Yield for Effective Results in 2025
In the realm of chemistry and various scientific applications, understanding how to calculate percent yield is essential for evaluating the success of chemical reactions and experiments. The **percent yield formula** is pivotal to this process, as it provides a quantitative measure of how efficient a reaction is. This article will thoroughly explore the concept of percent yield, its calculation methods, and its significance, ensuring you have all the knowledge needed for effective yield assessment in 2025.
Fundamentals of Percent Yield in Chemistry
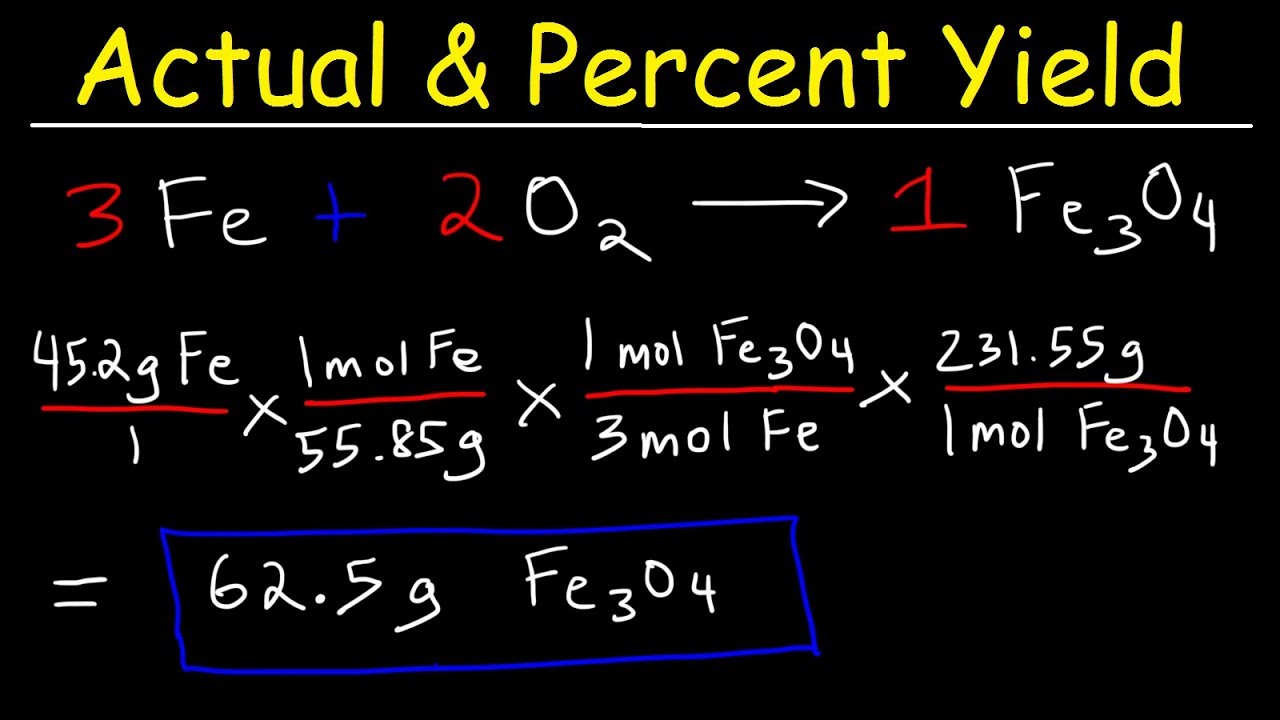
The **percent yield concept** is rooted in the difference between the theoretical and actual amounts of product generated in a chemical reaction. The **definition of percent yield** is given by the formula:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%
This calculation is crucial as it helps chemists determine **how effectively a reaction converts reactants into products.** Understanding this basic formula sets a foundation for **calculating percent yield** and exploring factors that may lead to discrepancies between the theoretical and actual yield.
Theoretical Yield vs. Percent Yield
To understand **theoretical yield vs. percent yield**, we must delve into how each is determined. Theoretical yield represents the maximum amount of product that can be generated based on the stoichiometry of the reaction, while percent yield reflects the actual quantity obtained in practice. Variations in these values can highlight potential losses during the reaction, such as incomplete reactions or side reactions consuming reactants. Tracking and analyzing this data through **percent yield calculations in lab experiments** can offer insights into the efficiency of the methodologies being used. For effective analysis, keeping accurate records of both actual and theoretical yields is essential.
How to Calculate Percent Yield
Calculating **yield percentage** involves several straightforward steps:
- Determine the theoretical yield based on the balanced chemical equation.
- Measure the actual yield obtained from the experiment.
- Plug these values into the percent yield formula.
As an example, if a reaction hypothetically yields 10 grams of product but only 8 grams are actually obtained, the percent yield calculation would be:
Percent Yield = (8 g / 10 g) × 100% = 80%.
This example illustrates how easily **calculating yield in chemistry** can indicate the performance of the reaction.
Challenges and Factors Affecting Percent Yield
While the concept of **determining percent yield** is relatively simple, many variables can impact the outcome. Historical **percent yield problems** can include human error in measurement, loss of material during transfer, or incomplete reactions. Understanding these (and actively mitigating the risks) can promote a higher yield percentage overall.
Common Factors Affecting Yield
A variety of aspects can lead to changes in **percent yield accuracy**, including temperature, pressure, reactant purity, and more. For example, in certain reactions, increasing the temperature might lead to higher kinetic energy, potentially enhancing reactant interaction and increasing the effective yield.
On the other hand, impurities in the reactants can reduce actual yields. By analyzing the laboratory setup and conditions, we can pinpoint factors affecting **yield performance analysis** and make informed improvements.
Improving Percent Yield
For those interested in enhancing their reaction outcomes, be it in academic or industrial settings, several **yield optimization techniques** can be deployed. These might not only focus on refining reaction conditions but also embedding more sophisticated techniques such as **data-driven yield estimates**. Strategies could include conducting preliminary reactions under varying conditions to observe their influence on yield, thereby informing subsequent trials.
Practical Applications of Percent Yield Calculations
The critical evaluations involved in **percent yield calculation in experiments** have vast applications in real-world scenarios, from laboratory chemistry processes to industrial manufacturing. Professionals must maintain standards to ensure quality, reproducibility, and efficiency throughout their processes, which is why **yield percentage trends** can serve as key performance indicators within their operations.
Real-World Percent Yield Examples
In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, calculating **average percent yield** can determine the viability of drug synthesis routes. If a certain pathway consistently delivers low percent yields, teams may need to re-evaluate their approach or reactant choices to tailor more efficient processes.
On a smaller scale, laboratory demonstrations can show how minimizing equipment or handling losses can lead to significant improvements in yield percentages. Proper application of the **percent yield explanation** can bridge the gap between theoretical modeling and real-world application.
Percent Yield Troubleshooting
Knowing how to address **percent yield issues** can be a game changer. Chemists often find that factors like improper calibration of measuring instruments, as well as atmospheric conditions around the reaction, can contribute to undesired outcomes in percent yield. Hence, employing regular calibrations, following method protocols, and maintaining a clean workspace can mitigate these challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the definitions and calculations regarding percent yield are essential for performance evaluation in chemical reactions.
- Several factors can influence the actual yield obtained, leading to variances in the expected results.
- Strategies are available for improving yield through optimization and careful analysis of experimental conditions.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of percent yield in chemical reactions?
The **significance of percent yield** lies in its ability to quantify the efficiency of a reaction, helping chemists and manufacturers improve processes and compare different synthetic routes over time. It serves as a key measure to reduce waste and optimize resource use.
2. What are the common reasons for low percent yield?
Common causes of **low percent yield** can include incomplete reactions, side reactions, and material losses during product isolation or purification processes. Recognizing these aspects is vital in refining methodology and anticipating outcomes.
3. How can I troubleshoot percent yield problems effectively?
**Percent yield troubleshooting** can be accomplished by auditing the entire experimental process for potential errors. It’s essential to ensure accuracy in measurements, utilize calibrated instruments, and meticulously maintain conditions consistent with successful prior experiments.
4. Can percent yield calculations vary in different types of reactions?
Yes, **yield calculations in practical terms** may vary significantly based on reaction conditions and materials used, making it crucial for researchers to understand their specific processes to accurately gauge percent yield outcomes.
5. How does theoretical yield impact percent yield calculations?
The **theoretical yield** serves as the benchmark against which **percent yield calculations** are assessed. A higher theoretical yield allows for a more effective analysis of actual yields, highlighting discrepancies and drawing attention to potential areas for improvement.
For more insights and resources related to yield and its calculations, please refer to our detailed articles on yield analysis and yield calculations in lab settings.