How to Properly Find the Volume of a Triangular Prism and Succeed in Geometry
How to Properly Find the Volume of a Triangular Prism
Understanding the Volume of a Triangular Prism
When it comes to the **volume of a triangular prism**, understanding its properties and the formulas used to calculate this volume is vital in geometry. A triangular prism is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel triangular bases and three rectangular faces connecting the corresponding sides. To find the volume, one must use an effective **triangular prism formula** that encompasses the base area and the height of the prism. This article will guide you through the steps necessary for **calculating the volume triangular prism**, complete with practical examples and applications.
The Prism Volume Formula Explained
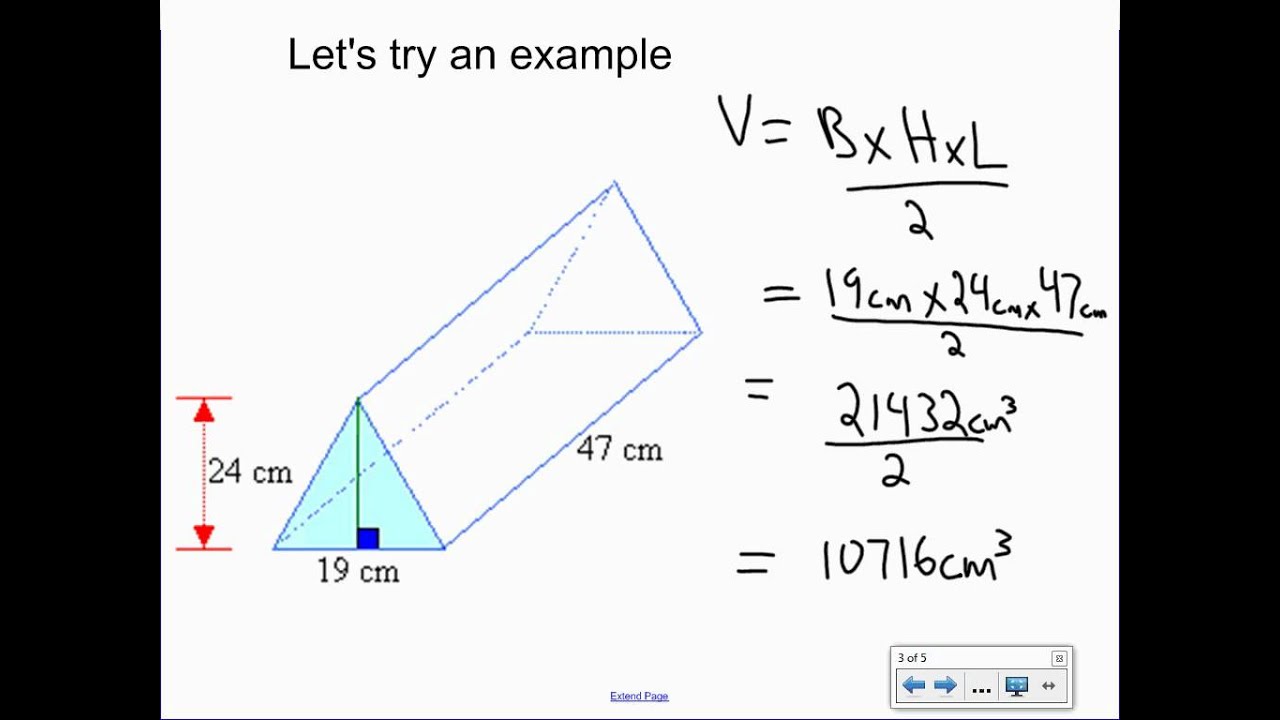
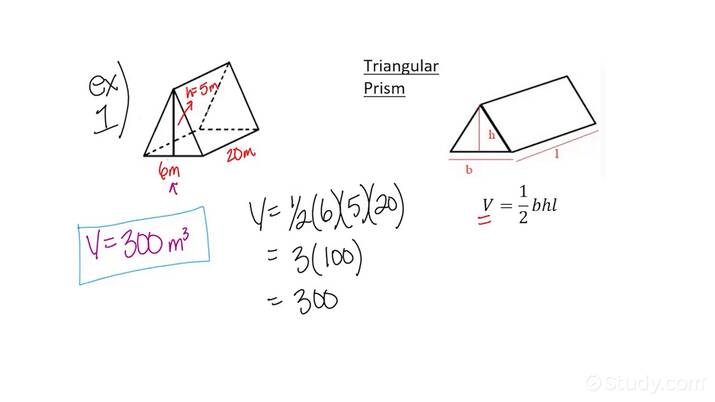
The formula to calculate the volume of a triangular prism can be summarized as follows: **Volume = Base Area × Height**. Here, the base area is calculated using the area of the triangular base, which can be obtained through the formula: **Area = 1/2 × base × height of the triangle**. It is important to note that when we refer to the height of the triangular prism, we mean the perpendicular distance between the two triangular bases. This relationship allows for easy calculation when the dimensions are properly understood. Remember, identifying the appropriate triangular prism dimensions is crucial for accurate volume calculations and is often represented as follows:
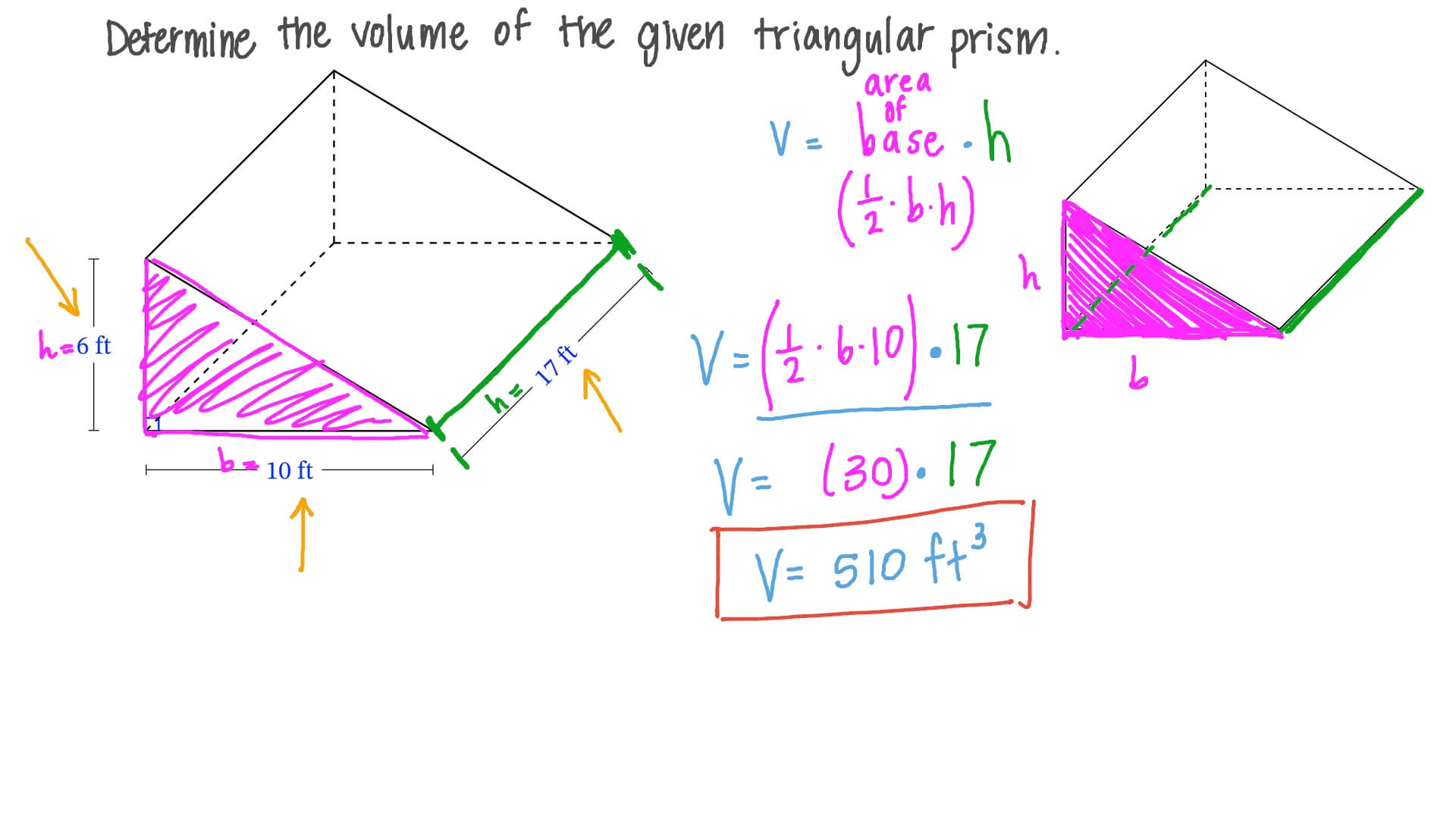
Example of Triangular Prism Volume Calculation
Let’s say we have a triangular prism where the base of the triangular face is 5 cm, the height of the triangle is 10 cm, and the height of the prism itself is 15 cm. To find the volume, follow these steps:
- Calculate the area of the triangular base:
Area = 1/2 × base × height = 1/2 × 5 cm × 10 cm = 25 cm². - Now, plug the base area into our volume formula:
Volume = Base Area × Height = 25 cm² × 15 cm = 375 cm³.
This example illustrates how essential it is to understand each segment of the **volume calculation** process for a triangular prism.
Triangular Prism Dimensions and Volume Calculation
Dimensions play a crucial role when talking about the **height of a triangular prism** and the subsequent volume calculations. A solid grasp of how to identify and measure these dimensions is necessary for both theoretical understanding and practical applications.
Measuring the Height of a Triangular Prism
To correctly measure the height of the prism, it is fundamental to identify the correct points of measurement. You will want to measure from the triangular base at a right angle to the opposite base. In contextual geometry, various aspects such as **height measurement** and understanding how it correlates with the triangular base are key to ensuring accurate volume analysis. Thus, students and practitioners alike need to practice identifying this height to achieve better precision in their **mathematical volume calculation**.
Applying Base Area Formulas
When calculating the volume of a triangular prism, determining the **area of triangular base** is the first step. Using the base area formula mentioned previously (Area = 1/2 × base × height), ensures you compute correctly. If given the vertices of a triangle or coordinates, you might consider using Heron’s formula or the coordinate geometry approach for base area calculations. Effective practice and ample examples of triangular area calculation are crucial in solidifying understanding.
Real-Life Applications of Triangular Prisms
The **volume of different prisms**, including triangular prisms, is not merely a theoretical exercise; it manifests in various real-life contexts. Understanding these applications can often provide motivation and relevance for students learning geometry.
Geometry in Architecture and Design
In architecture, the application of geometric principles is prolific. The structures often incorporate triangular prisms to maintain stability and provide aesthetic value. The knowledge of **calculating shapes** is indispensable for architects who not only need to visualize 3D shapes but also calculate the volumetric spaces they are designing. Additionally, engineering fields exploit **volume in physics** through triangular prisms to optimize load distributions and create robust designs. Thus, practicing **geometry formulas** becomes invaluable in many professional environments.
Education and Practical Geometry Problems
In educational contexts, teaching students how to determine the volume of a triangular prism helps develop essential problem-solving skills. Schools often implement exercises, such as calculating **volume measurement** or solving **practical geometry problems**, alongside using **triangular prism volume calculators** to enhance their understanding of geometric principles. Such exercises foster not only cognitive growth but also enthusiasm for mathematics, as students explore **applications of prisms** in the real world.
Key Takeaways
- Gaining a sound understanding of the **triangular prism volume** fundamental formula is key.
- Proper measurement of both the triangular base and height is essential for calculating volume accurately.
- Recognizing the real-life applications of triangular prisms enhances comprehensibility and interests students.
- Practical problem-solving involving the calculations of triangular area and volume strengthens geometric skills.
FAQ
1. How do I calculate the area of a triangle?
To find the area of a triangle, you use the formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height. This means you multiply the base of the triangle by its height and then divide by two. This basic concept is fundamental when tackling more complex volume calculations in geometry.
2. What units are used for measuring volume?
Volume is typically measured in cubic units, such as cubic centimeters (cm³), cubic meters (m³), or liters. It’s important to maintain consistent units across your calculations to arrive at valid results when working with geometric volumes.
3. Are there different types of triangular prisms?
Yes, triangular prisms come in various types, primarily defined by the shape of their triangular bases. These can include right triangular prisms, isosceles triangular prisms, and scalene triangular prisms, each possessing different characteristics affecting their volume calculations.
4. How does the volume of a triangular prism differ from other prisms?
The primary distinction in volume calculation comes from the type of base each prism has. While every prism’s volume is derived from the formula: Volume = Base Area × Height, the base area formulation will vary by the shape of the base, being triangular in this case.
5. Why is knowing the volume of a triangular prism important in real life?
Understanding the volume of a triangular prism is crucial in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and design where space optimization is key. It plays a significant role in ensuring proper load support, maximizing storage capacity, and creating functional designs.