How to Understand How Long it Takes for Caffeine to Kick In: Discover the Secrets in 2025
How Long Does Caffeine Take to Kick In?
Caffeine is one of the most widely consumed stimulants worldwide, known for its ability to enhance alertness and energy levels. Understanding how long caffeine takes to kick in is crucial for optimizing its benefits. The timing of caffeine absorption and its effectiveness can vary significantly from person to person depending on multiple factors. In this article, we will explore the caffeine absorption time, the factors that influence its effectiveness, and the underlying science that explains the effects of caffeine onset.
The Science of Caffeine Timing
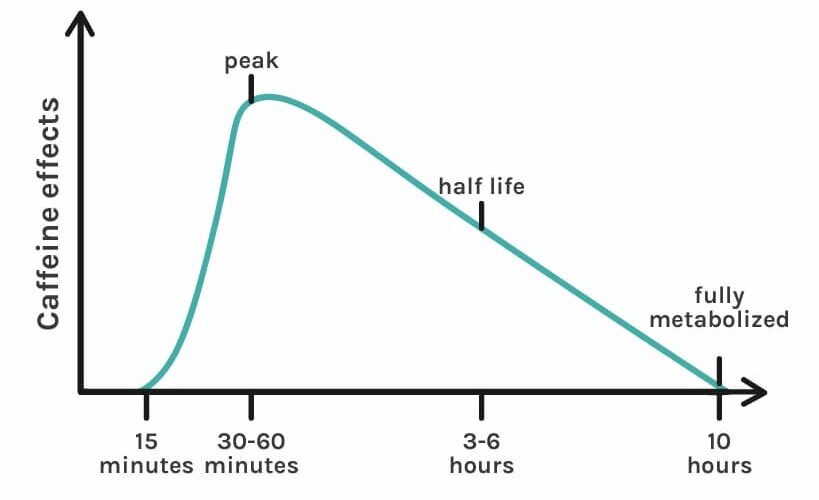
Caffeine’s ability to enhance alertness and boost energy is well-documented, but the caffeine activation period and onset time can vary. Typically, caffeine begins working within 15 to 45 minutes after consumption, reaching peak effectiveness around 30 to 60 minutes post-ingestion. This variance is primarily due to individual differences in caffeine metabolism rate and factors such as body weight, age, and habitual caffeine consumption.
How Quickly Does Caffeine Work?
The speed of caffeine effects largely depends on its absorption into the bloodstream. After ingestion, caffeine passes quickly through the gastric system, promoting a quick onset of stimulation once it enters the bloodstream. For example, someone drinking a strong cup of coffee may start feeling heightened energy and focus much faster than someone consuming caffeine from tea, which has lower concentrations. Understanding how fast caffeine starts working can help with timed consumption to maximize productivity.
Factors Affecting Success of Caffeine Onset
Many factors impact caffeine response time, including genetics, lifestyle, and even diet. Individuals with higher caffeine tolerance may experience delayed effects, while those with lower tolerance could feel the effects more rapidly and intensely. Frequent caffeine consumers can also develop a level of resistance, affecting the time for caffeine effects to be felt. Additionally, food intake can influence absorption rates—consuming caffeine on an empty stomach may lead to faster effects compared to taking it with food.
Caffeine Effects Duration and Beyond
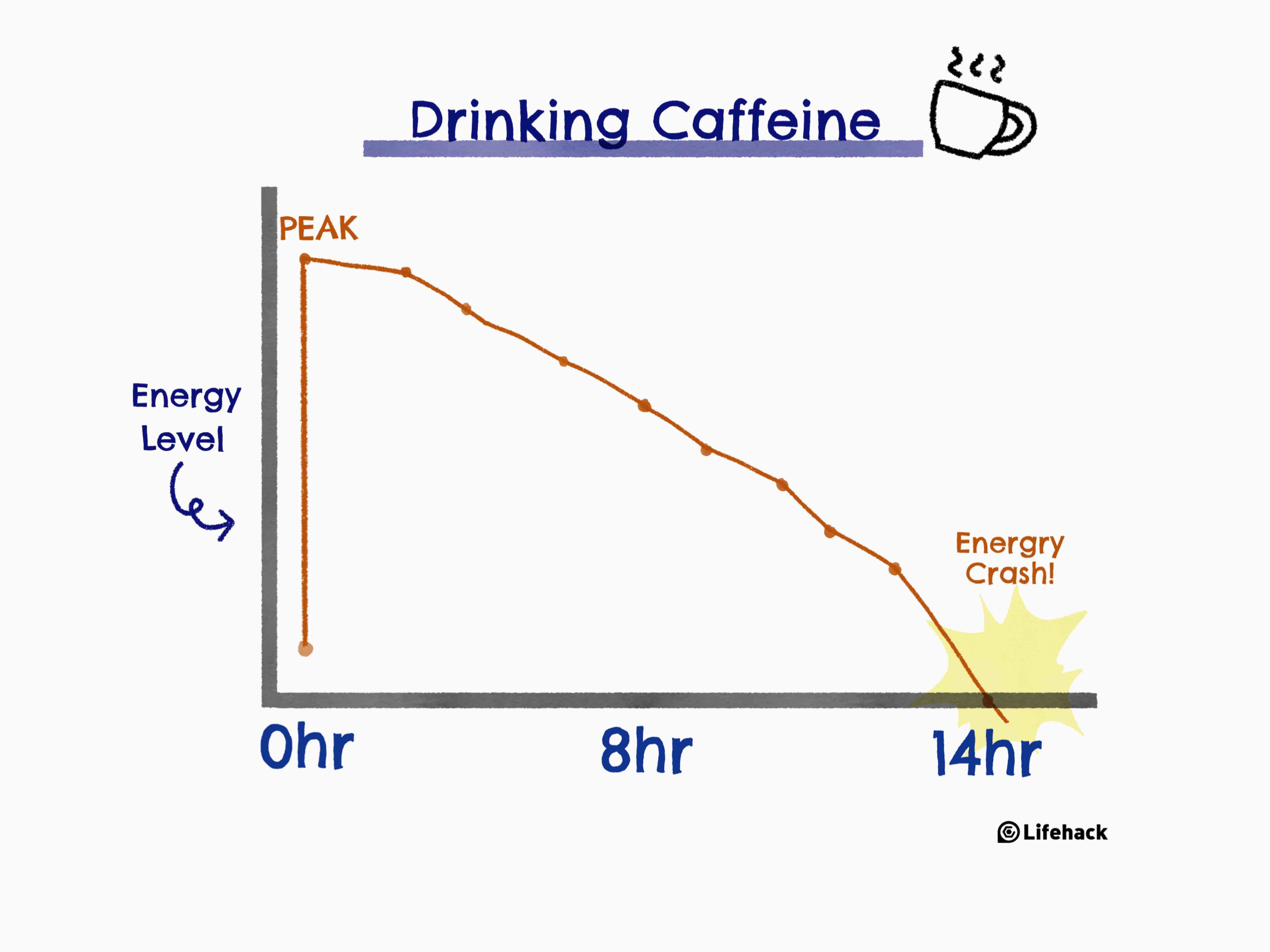
Understanding the duration of caffeine’s effects is crucial for both sports performance and daily productivity. Generally, caffeine can maintain heightened levels of alertness for several hours, with effects lasting 3 to 5 hours after a typical dose. However, caffeine effects duration can be influenced by various individual factors such as metabolism and overall health, leading some to experience prolonged or diminished effects.
Caffeine’s Impact on Energy Levels
Energizing effects of caffeine peaks within an hour after consumption; however, the way it enhances caffeine and energy levels greatly varies. Research indicates that periods of increased alertness may also include short bursts of focus and energy followed by potential fatigue. It is essential to learn how caffeine plays its role in maintaining energy levels and when to consume it. For example, athletes often schedule caffeine before workouts for its maximal performance-enhancing effects.
Caffeine Half-Life and Metabolism
The caffeine half-life, which typically ranges from 3 to 7 hours, provides insight into how long it takes for caffeine levels to decrease by half within the body. Variability in the body’s processing of caffeine reflects individual physiological differences and overall health. For instance, individuals with liver conditions may experience a slower metabolism rate, time for caffeine effects extending beyond typical expectations. Knowing your unique caffeine metabolism rate can help tailor timely doses for optimal performance.
Practical Strategies for Effective Caffeine Use
Implementing caffeine timing strategies into daily routines can significantly help manage energy levels and productivity. Whether you’re studying, working, or exercising, knowing the best times to consume caffeine can maximize its benefits. For example, strategizing consumption ahead of critical tasks can ensure peak alertness when needed most. Incorporating caffeine into a pre-designed routine based on personal experience can offer substantial help.
Maximizing Caffeine Effectiveness
To maximize the effectiveness of caffeine, measure and track your intake thoroughly. Being aware of various caffeine types can also aid in this process. For instance, one may prefer coffee, with its higher caffeine content, for quicker effects, while others might opt for tea for a more balanced, sustained boost. A comprehensive understanding of caffeine consumption allows individuals to customize their experiences based on their specific needs and preferences.
Addressing Caffeine Fatigue and Withdrawal
Caffeine isn’t without potential downsides; excessive consumption can lead to withdrawal symptoms and fatigue. It’s essential to be mindful of the daily limits and cyclical consumption patterns to avoid diminishing returns from overstimulation. Establishing a moderate, balanced approach, with attention to caffeine withdrawal symptoms, helps sustain energy levels without severe fluctuations or crashes.
Key Takeaways
- Caffeine typically kicks in between 15 to 45 minutes after consumption.
- Factors affecting how long caffeine takes to work include individual metabolism, tolerance, and food consumption.
- The effects of caffeine can last between 3 to 5 hours, depending on individual health and consumption habits.
- Implementing caffeine timing strategies can enhance performance and energy levels.
- Moderation is crucial to avoiding withdrawal symptoms and maintaining optimal effects.
FAQ
1. What is the average time for caffeine effects to begin?
The average time for caffeine effects to begin is typically around 15 to 45 minutes. However, this can vary widely based on individual metabolism and the form in which caffeine is consumed.
2. How does caffeine absorption differ between various drinks?
Caffeine absorption can differ significantly depending on the drink; coffee often leads to quicker onset due to higher caffeine levels while tea provides a more gradual effect owing to lower concentrations and other compounds.
3. Can factors like diet impact caffeine effectiveness?
Yes, consuming caffeine on an empty stomach usually results in quicker absorption and more visible effects. In contrast, having it with food can slow down absorption and delay the onset of effects.
4. Is there a safe limit for daily caffeine intake?
Most health authorities suggest that up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is considered safe for most adults, equivalent to about 4 cups of brewed coffee.
5. How do individual differences affect caffeine tolerance?
Individual differences, such as genetics, lifestyle, and potential health conditions, can all contribute to how one develops caffeine tolerance, influencing both the effects experienced and the recommended daily dosages.
6. At what time should I consume caffeine for maximum productivity?
The optimal times for caffeine consumption often depend on individual schedules and the nature of tasks at hand. Generally, consuming caffeine 30 to 60 minutes before a challenging task can help maximize alertness and focus.
7. What alternative sources of caffeine should I be aware of?
Caffeine is not just found in coffee; it’s also present in tea, energy drinks, and soft drinks, as well as in certain foods like chocolate. Being aware of these sources can help manage overall caffeine consumption.